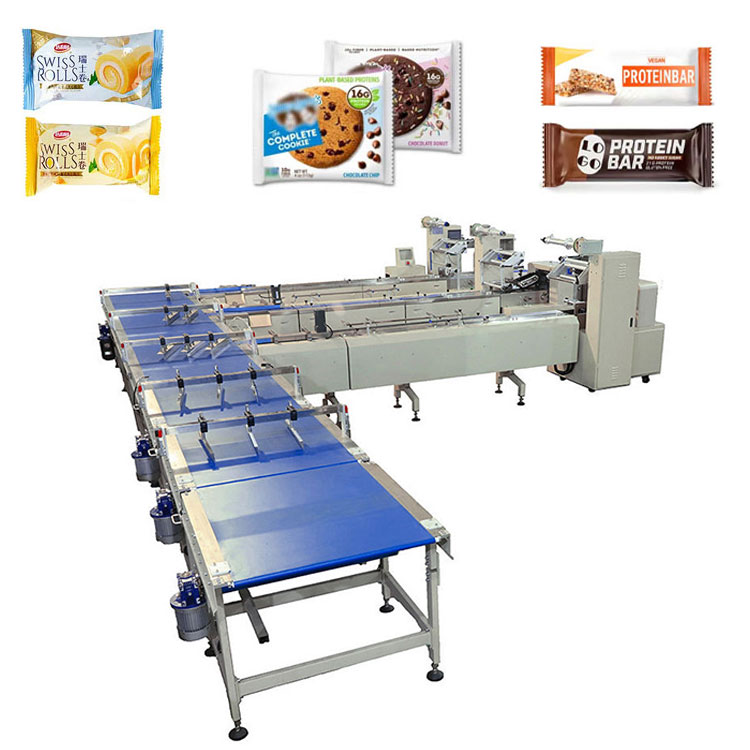
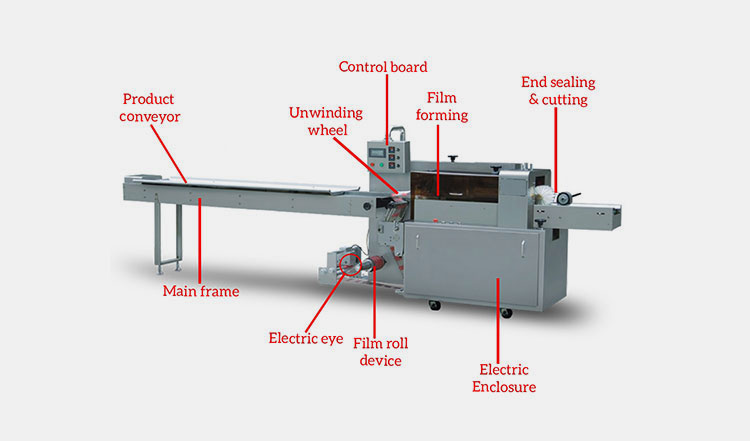
In the competitive frozen food market, safeguarding product quality and extending shelf life isn’t just an advantage—it’s essential for your brand’s reputation and profitability. The heart of this protection lies in advanced frozen food packaging machines, designed to maintain product integrity even at extreme temperatures, such as the -30℃ required for specialized PP trays.
This comprehensive guide will navigate the intricate world of frozen food packaging machines, detailing crucial types like VFFS systems capable of 20-100 bags per minute, exploring the specialized materials essential for low-temperature integrity, and offering a clear framework for selecting the ideal equipment.
Visit https://chlbgroup.com/ to consult with our packaging experts and build a more efficient, future-ready frozen food operation.
Why is High-Quality Frozen Food Packaging Crucial?
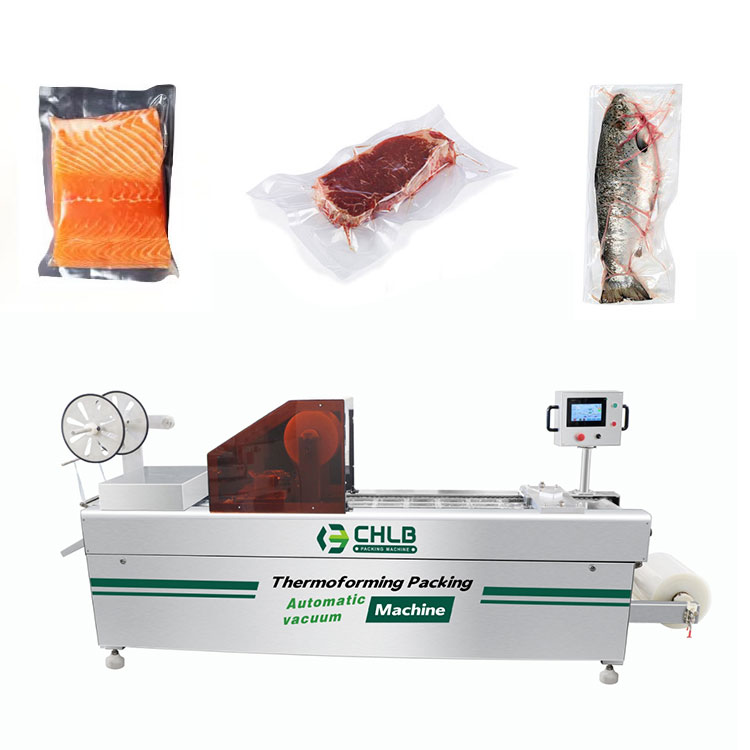

High-quality frozen food packaging is crucial for preventing quality degradation by providing barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and physical damage. It minimizes freezer burn, ensures product safety, and extends shelf life during storage at -24℃ to -18℃ and transport. This is achieved through advanced material science, adherence to strict regulatory standards like GB 9685-2016 and FDA limits, and rigorous performance testing.
Essential Role in Product Integrity and Preservation
Provides critical barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and physical damage, preventing quality degradation and flavor loss.
Mitigates freezer burn and reduces contamination risks during extended storage at -24℃ to -18℃.
Ensures product safety and maintains an extended shelf life throughout freezing, storage, and transport, thereby preventing economic losses from spoilage.
Compliance, Advanced Materials, and Rigorous Performance
Employs specialized materials like PET/PE, BOPP/PE, and BOPP/CPP, offering cold-resistant properties, low-temperature heat-sealing, and high tensile strength.
Adheres to stringent regulatory standards such as GB 9685-2016 for additive limits and FDA migration limits (e.g., 10 ppb for high-exposure scenarios).
Verifies performance through rigorous testing for barrier properties, puncture resistance, and compression (per SN/T0715-1997) using specialized equipment like oxygen/water vapor transmission rate testers.
Incorporates food-grade PP trays capable of withstanding temperatures as low as -30℃ without brittleness.
What is Frozen Food Packaging?
Defining Frozen Food Packaging
Engineered food-contact materials and structures (bags, lidding, trays, and outer corrugated boxes) for frozen products.
Designed to maintain mechanical integrity, barrier performance, and safety from deep-freezing through distribution and thawing.
Comprises primary packaging (flexible films for individual items, trays for portions) and secondary/tertiary packaging (e.g., corrugated outers).
Essential Materials, Technical Requirements & Regulatory Standards
Common flexible film structures include PET/PE, BOPP/PE, BOPP/CPP, NY/PE, and PET/NY/AL/PE for varied barrier and strength needs.
Tray materials typically include food-grade PP (suitable down to -30°C) and PET for stiffness and clarity.
Inner layers often feature LLDPE, EVA, or nylon (PA) to ensure low-temperature toughness, tear, impact, and puncture resistance.
Functional requirements encompass resistance to low and high temperatures, sufficient mechanical strength, chemical resistance to acids/oils, and strict hygiene.
Key regulatory compliance examples: China’s GB 9685-2016, GB 4806.7-2016, and GB/T 10004-2008; US FDA Title 21 CFR (specifically Parts 177 e 186 for plastics).
Advantages of Frozen Food Packaging
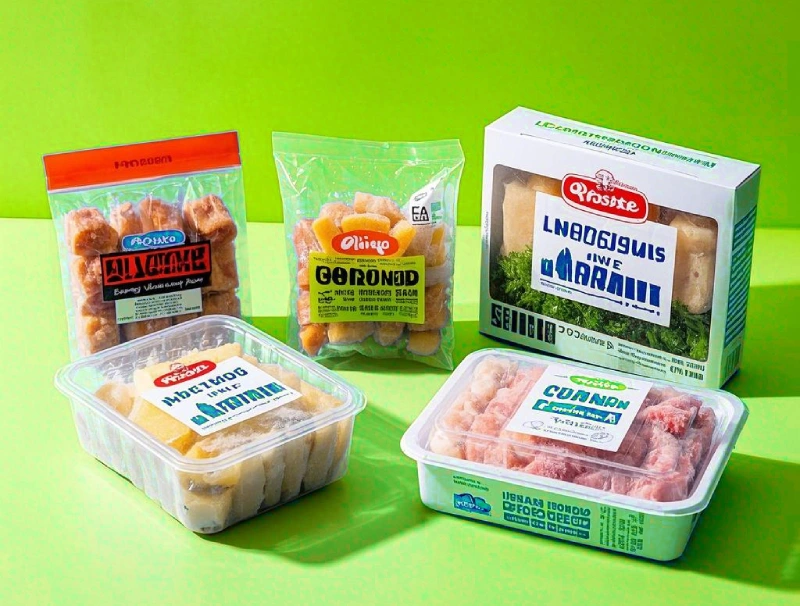

High-quality frozen food packaging leverages advanced materials and precise engineering to prevent freezer burn, retain nutrients, and extend shelf life by maintaining barrier integrity at subzero temperatures. It also offers significant logistical advantages through optimized design and supports high-speed processing.
Enhanced Product Integrity & Extended Shelf Life
Flexible packaging engineered for resistance to moisture and oxygen to prevent freezer burn and nutrient loss.
Vacuum-pack formats achieve Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR) < 1 cc/m²/day, significantly limiting oxidation.
Embalagem de atmosfera modificada (MAP) systems achieve ≥98% gas replacement rate for color and quality stability in fruits and vegetables.
Directly contributes to reduced freezer burn, better color retention, and extended shelf life for meats, seafood, and produce.
Optimized Material Performance & Cold Chain Logistics
Packaging materials and machine components remain functional in operating temperature ranges from -40°C to -18°C.
Multilayer film structures (e.g., PET/PE, BOPP/PE, NY/PE) provide moisture barrier, low-temperature heat seal, and puncture resistance.
Film thickness of ≥80 μm is recommended for sharp frozen products to ensure puncture resistance.
Lightweight flexible pouches and films reduce shipping weight and freezer space.
Automatic vacuum machines achieve throughputs of 30–50 bags/min, and tray sealers run at 15–30 trays/min.
Boost Your Productivity with Intelligent Packaging Automation

Common Frozen Foods and Their Packaging Considerations

Different frozen foods, from bulk vegetables to prepared meals, demand distinct packaging solutions. These range from simple PE bags for low-barrier products to complex multilayer laminates and rigid PP trays for higher-value items, all designed to ensure product integrity, shelf life, and compliance with strict food-contact regulations.
Tailoring Packaging to Specific Frozen Food Categories
Low-barrier products such as bulk frozen vegetables commonly use single-layer PE bags (e.g., LDPE/LLDPE) for basic moisture protection.
Higher-value items like dumplings, seafood, and prepared meals typically utilize multilayer laminates (e.g., PET/PE, BOPP/PE, NY/PE/LLDPE) for enhanced protection.
Rigid containment in PP thermoformed trays is common for ready meals, meat, and fish, often paired with an overwrap or lid.
Where freezer burn, aroma retention, or long export cycles are critical, structures with VMPET or AL (e.g., PET/VMPET/CPE, PET/NY/AL/PE) are chosen.
Key Packaging Material Structures and Performance Requirements
Composite flexible bags like OPP/LLDPE and NY/LLDPE are used where moisture, cold resistance, and puncture resistance are paramount.
Aluminized structures (e.g., PET/VMPET/CPE) provide high barrier and premium graphics, despite poorer low-temperature sealability and higher cost.
Inner layers often include LLDPE, EVA, or nylon (PA/NY) as co-extruded or laminated components to enhance low-temperature impact and tear resistance.
Food-grade PP (polypropylene) trays are suitable for frozen applications, usable at temperatures down to −30 °C.
Corrugated boxes are the dominant transport packaging for frozen foods due to requirements for shock absorption and compression strength.
Detailed Explanation of Mainstream Frozen Food Packaging Machine Types
Mainstream frozen food packaging machines encompass VFFS (Vertical Form Fill Seal) for granular IQF products, HFFS (Horizontal Form Fill Seal) for solid items, pre-made pouch machines for premium products, vacuum packaging for extended shelf life, and cartoning machines for secondary packaging. These systems are designed for high efficiency, hygiene, and precise handling of frozen goods, utilizing advanced automation for consistent output.
| Machine Type | Primary Application | Key Performance/Specs |
|---|---|---|
| VFFS (Vertical Form Fill Seal) | IQF granules/pieces (fruits, fries, dumplings) | 20-100 bags/min; bag widths 50-350mm, lengths 80-450mm, film 0.04-0.09mm |
| HFFS (Horizontal Form Fill Seal) / Flow Wrappers | Solid, regularly shaped products (ice cream bars, patties) | 30-200 packs/min (high-speed >200/min); horizontal wrapping |
| Pre-made Pouch Machines | Higher-value products, stand-up/zipper pouches | 15-60 pouches/min; auto pick-open-fill-seal |
| Vacuum Packaging Machines | Ready meals or meat products, extended shelf life (MAP optional) | 5-30 trays/min; air evacuation |
| Cartoning Machines | Secondary packaging for bagged/trayed items | 20-150 cartons/min; protection and logistics |
Core Packaging Machine Types and Their Primary Applications
**VFFS (Vertical Form Fill Seal)** machines are ideally suited for Individually Quick Frozen (IQF) granular and piece products, including items like frozen fruits, French fries, or dumplings. These systems form bags vertically from a roll of film, creating various styles such as pillow or gusseted bags, and are highly efficient for free-flowing frozen goods.
**HFFS (Horizontal Form Fill Seal) / Flow Wrappers** are designed for solid, regularly shaped frozen products. This category includes items such as ice cream bars, frozen patties, or pre-made pastries, which are wrapped horizontally using a continuous film feed, ensuring a snug and secure package.
**Pre-made Pouch Machines** cater to higher-value frozen products where presentation and functionality are key. These machines automatically pick, open, fill, and seal pre-formed pouches, including stand-up and zipper bags, offering convenience and a premium aesthetic to the consumer.
**Vacuum Packaging Machines** are primarily utilized for frozen ready meals or meat products. Their core function involves evacuating air from the package to prevent freezer burn and significantly extend shelf life. Many models also offer Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) capabilities for enhanced preservation.
Performance Metrics, Automation, and Operational Specifications
Regarding **Speed & Capacity**, VFFS machines typically operate at 20-100 bags per minute, while HFFS models can achieve 30-200 packs per minute, with high-speed variants exceeding 200 packs/min. Pre-made pouch machines generally run at 15-60 pouches per minute, vacuum packaging systems at 5-30 trays per minute, and cartoning machines at 20-150 cartons per minute, depending on product and configuration.
For **Bag/Film Specifications**, VFFS machines commonly accommodate bag widths between 50-350mm and lengths from 80-450mm. They are compatible with various film types, such as OPP/CPP and PET/PE, with film thicknesses typically ranging from 0.04-0.09mm to ensure durability and seal integrity in freezing conditions.
High levels of **Automation & Control** are standard, featuring modular designs, servo-driven transport systems for smooth product handling, and PID temperature control for precise and consistent sealing. These technological advancements enable quick changeovers, often completed within 5-10 minutes, optimizing production efficiency.
How to Choose the Most Suitable Frozen Food Packaging Machine?
Choosing the right frozen food packaging machine involves evaluating product characteristics (size, fragility, flowability), desired production speed (20-100 bags/minute), and required automation. Key considerations also include selecting appropriate machine types like VFFS for IQF products or HFFS for solid items, and ensuring compatibility with low-temperature materials (PE, PP, PET with barriers) and strict hygiene standards (food-grade stainless steel, GMP).
| Criterion | Key Specification/Detail | Notes/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Production Efficiency | 20-100 bags/minute | For VFFS machines; depends on bag size, product, and dosing equipment. |
| Machine Construction & Hygiene | Food-grade stainless steel | Required for hygienic design, GMP standards, and CIP/SIP cleaning capabilities. |
| Packaging Film Materials | PE, PP, PET, plus composites (EVOH or PA barriers) | For low-temperature flexibility, puncture resistance, and heat sealability. |
| Laminate Structures | BOPP/PE, BOPP/CPP | For moisture-proofing, cold resistance, and high low-temperature heat-sealing tensile strength. |
| Enhancing Material Additives | Nylon, LLDPE, EVA | For enhanced low-temperature resistance, tear resistance, impact resistance, waterproofing, and gas barrier properties. |
| Material Temperature Tolerance | -30℃ | Operational tolerance for food-grade PP materials. |
| Machine Type by Product | VFFS, HFFS/Flow Wrappers | VFFS for IQF loose products; HFFS for solid items (e.g., ice cream bars, patties). |
Assessing Your Product & Production Needs
Evaluate product traits: size, shape, weight, fragility, flowability, and temperature sensitivity.
Determine required automation level (semi-automatic to PLC-integrated systems) based on production volume and scalability goals.
Consider desired packaging formats (e.g., pillow bags, stand-up pouches) and target output speed.
Matching Machine Types, Materials & Hygiene Standards
Select Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) machines for IQF loose products; HFFS/Flow Wrappers for solid items like ice cream bars or patties.
Ensure machine construction is food-grade stainless steel, meeting GMP standards with CIP/SIP capabilities.
Choose packaging films like Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyester (PET), often with EVOH or PA barrier layers for low-temperature flexibility, puncture resistance, and heat sealability.
Utilize laminates (e.g., BOPP/PE, BOPP/CPP) for economical moisture-proofing, cold resistance, and high low-temperature heat-sealing tensile strength (operational tolerance for food-grade PP at -30℃).
Target production efficiency between 20-100 bags/minute, depending on bag size, product, and dosing equipment.
Conclusion: Elevate Your Frozen Food Business with the Right Packaging Machine from CHLB Packing

Defining the ‘Right’ Frozen Food Packaging Solution
The ‘right’ machine aligns with critical industry benchmarks for speed, dosing accuracy, film/pouch range, hygiene, utility efficiency, and long-term lifecycle support. It must integrate seamlessly into complete production lines, encompassing multihead weighing, vacuum/MAP options, and secondary packaging like cartoning and case packing. This strategic investment directly leads to higher throughput, minimized product giveaway, and ensures packaging is compliant with regulatory standards, boosting market competitiveness.
CHLB’s Technical Superiority: Performance, Hygiene & Integration
CHLB offers high-speed VFFS (20–100 bags/min) and HFFS/flow wrappers (30–200 packs/min) for diverse frozen products, from IQF vegetables to ready meals. Our machines handle robust material specifications, including film webs up to 720 mm and laminate thicknesses in the 40–90 μm range for varied pack sizes and barrier levels. Prioritizing hygiene, CHLB’s equipment features stainless steel product-contact parts, enclosed drive systems, and options for ultra-clean zones, aligning with strict food safety regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does product brittleness at low temperatures affect machine performance and film choice?
At typical frozen-food conditions of −18 to −30 °C, products become hard and sharp while packaging films lose impact strength, increasing punctures, seal cracking, and jams. To mitigate this, frozen lines generally specify films whose brittle temperature is at least 10–15 °C below the lowest product temperature (≈−35 to −40 °C).
What is the ROI timeline for investing in automated frozen food packaging machinery?
The industry standard ROI timeline for investing in automated packaging machinery, including for frozen food operations, is a payback period of 6 months to 2 anos. High-volume production lines can often achieve ROI within 6-12 months, while more complex and integrated systems may take up to 2 years to realize their return on investment.