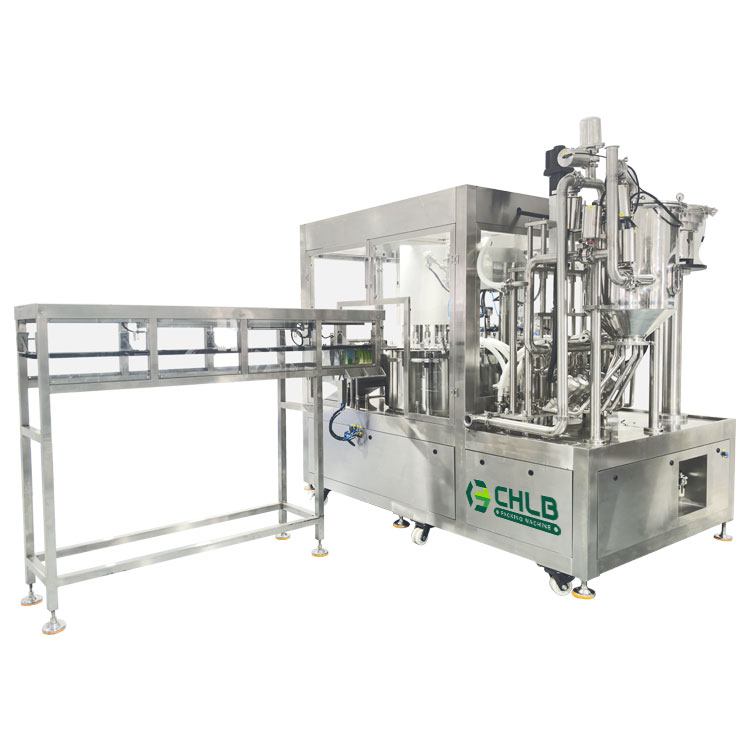
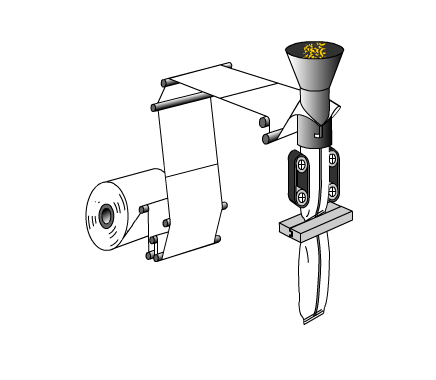
Choosing the right food packaging machine today is about much more than production speed. Manufacturers must balance food safety, automation efficiency, and growing sustainability requirements—while staying compliant with stricter industry standards.
This guide explains food packaging machines in clear, practical terms—from common systems like VFFS and horizontal flow wrappers to automation levels, product compatibility, and key food safety standards such as FDA and ISO 22000. We also break down real ownership costs and future-ready packaging trends.
At CHLB Group, we help food producers choose and integrate packaging solutions that fit their products, production goals, and long-term growth. Visit us to speak with our packaging specialists and explore tailored food packaging systems.
Navigating the 2026 Food Packaging Landscape
The 2025 food packaging landscape is characterized by stringent hygienic design standards (SS304/SS316, IP67-IP69K), advanced high-speed automation integrating AI and IoT, and a strong push towards sustainability-ready materials and traceable labeling to meet evolving consumer and regulatory demands.
Hygienic Design & Regulatory Compliance
Materials & Construction: Primary food-contact and washdown areas utilize AISI 304 and 316 stainless steel (SS304/SS316) with sloped surfaces and minimal crevices for sanitary design.
Ingress Protection: Robotics and enclosures aim for IP67–IP69K ratings to endure high-pressure, high-temperature washdown and caustic Clean-in-Place (CIP) chemicals.
Regulatory Alignment: Machines are engineered to comply with FDA, USDA sanitary expectations, HACCP, ISO-based food safety schemes, and the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
High-Speed Automation & Sustainable Innovations
Throughput & Line Capacity: VFFS systems like the Bosch SVE 2520 DZ achieve up to 300 bags per minute; automated lines process thousands of units per hour with servo-driven controls.
Automation Stack: Integration of servo motors, pneumatic actuators, vision systems, PLC/HMI controls, IoT sensors, and AI-based inspection for defect detection and traceability.
Sustainability Compatibility: New systems handle recyclable films, paper-based trays, compostable, and biodegradable films, requiring optimized sealing temperatures and pressures.
Industry Investment: PMMI’s ‘State of the Industry 2025’ report highlights capital shifts towards sustainability-ready machinery, higher automation, and IoT-enabled lines.
Classification: Vertical vs. Horizontal vs. Rotary
Food packaging machines are fundamentally classified by their mechanical architecture: Vertical (VFFS) uses gravity for compact, downward film and product flow; Horizontal (HFFS) moves products and film horizontally for high-speed, stable wrapping; and Rotary employs a circular turret for multi-station processing of premade pouches or rigid containers, optimizing space. Each excels in different applications based on product type, speed, and footprint.
| Machine Type | Operational Principles & Performance | Suitable Products & Footprint |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS) | Uses gravity for downward film and product flow. Film unwinds, forms a tube, product drops, then sequential vertical sealing/cutting. Throughput: 150–300 bags/min. | Ideal for products that flow (powders, granules, liquids, frozen items, snacks, coffee, sugar, rice). Compact, low-footprint, tall-and-narrow design; requires less floor space than horizontal for equivalent capacity. |
| Horizontal Flow-Wrap (HFFS) | Product and film move horizontally. Product pushed/conveyed into film tube, sealed longitudinally and at ends. Product is supported for stable high-speed handling. Throughput: >400 bags/min for standardized items. | Optimal for single, solid items (e.g., cereal bars, bakery products) where geometry preservation is critical. Generally requires more linear space compared to VFFS for equivalent capacity. |
| Rotary Architecture | Utilizes a circular turret indexing products/pouches through 6–12 radial stations for open, fill, seal, etc. Premade-pouch throughput: ≤60 bags/min. Rotary indexing for cups/trays provides high-speed, high-volume production. Washdown-ready design for rigid containers. | Suitable for premade pouches (versatile formats, flexible fill volumes) and rigid containers (cups, bowls, trays, medical-nutrition containers). High function density in smaller square/circular footprints; optimizes space. |
Core Architectural Principles & Product Flow
Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS): Film unwinds downward, wraps a forming tube, product drops by gravity, followed by sequential vertical sealing and cutting. Favors products that flow (powders, granules, liquids, frozen particulates).
Horizontal Flow-Wrap (HFFS): Product and film move along a horizontal axis; product is pushed or conveyed into a film tube, sealed longitudinally on the underside, and then end-sealed by rotating or reciprocating jaws. Ideal for single, solid items.
Rotary Architecture: Utilizes a circular turret or turntable that indexes products or premade pouches through multiple radial stations (typically 6–12) for operations like opening, filling, sealing, and optional checks. Concentrates many operations into a compact footprint.
Operational Throughput, Application, and Space Efficiency
Vertical (VFFS): Throughput of 150–300 bags/min; suitable for diverse products like snacks, coffee, sugar, and frozen items. Offers a compact, low-footprint, tall-and-narrow design, requiring less floor space than horizontal for equivalent capacity.
Horizontal (HFFS): Achieves >400 bags/min for standardized items (e.g., cereal bars, bakery products); optimal for high-volume runs of solid, uniform products where geometry preservation is critical. Products are supported, allowing stable high-speed handling.
Rotary (Premade Pouch/Rigid Containers): Premade-pouch versions typically reach ≤60 bags/min; rotary indexing for cups/bowls/trays provides high-speed, high-volume production. Offers high function density in smaller square/circular footprints. Rotary premade-pouch machines allow more flexible filling volumes, though high fill weights may require speed reductions due to centrifugal forces, where horizontal premade-pouch lines can be more stable.
Intelligent Packaging Machinery: Precision, Performance, Profit.

Matching Machine Type to Product Consistency (Solid vs. तरल)
Machine selection for packaging hinges primarily on product rheology—its viscosity, presence of particulates, and flow behavior. Free-flowing solids typically use gravity-fed VFFS systems with multihead weighers, while liquids and semi-solids require positive-displacement pumps and specialized hygienic materials like SUS316 stainless steel.
| Product Consistency | Typical Machine & Dosing System | Key Features & Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Free-flowing Solids (Granulates, Powders, Piecewise) | VFFS/HFFS or can/bottle lines with Multihead Weighers, Auger Fillers, or Volumetric Cup Fillers. | Gravity-fed, high-speed continuous motion (up to 300 bags/min/tube), suitable for snacks, confectionery, frozen foods. |
| Viscous Liquids & Semi-solids (Pastes, Gels, Particle-containing) | Multilane Sachet/Stick-pack/Pouch machines with Servo Piston, Gear, or Rotary Pumps. | Positive-displacement metering, intermittent motion (40-80 cycles/min), SUS316 product-contact parts, GMP/CE/CUL compliant. |
Differentiating Packaging Systems by Product Rheology and Form
The primary engineering discriminator for machine type is product rheology (viscosity, presence/size of particulates) and its form (free-flowing solid, powder, liquid, or paste).
Free-flowing solids like snacks, candies, nuts, and powders are typically handled by VFFS or horizontal systems, utilizing gravity-fed or auger dosing mechanisms.
Viscous liquids and semi-solids (e.g., sauces, gels, creams) necessitate positive-displacement metering and a hygienic, corrosion-resistant product path.
Specialized Machine Configurations for Liquid, Semi-Solid, and Dry Product Handling
Liquid and semi-liquid machines (e.g., multilane sachet systems) use servo piston, servo gear, or servo rotary pumps to handle viscosities from 5–50,000 cP, including particle-containing pastes.
Product-contact parts for liquids often require SUS316 stainless steel to meet GMP and CE requirements for hygienic and corrosion-resistant operation.
Solid product handling (granulates, powders, piecewise solids) employs VFFS systems with multihead weighers, auger fillers for powders, or volumetric cup fillers for granulates.
Output capabilities vary: high-speed VFFS for free-flowing solids can reach up to 300 bags/min per tube, while liquid/paste multilane sachet machines typically achieve 40–80 cycles/min.
Choose the Right Packaging Machine for Your Food Business
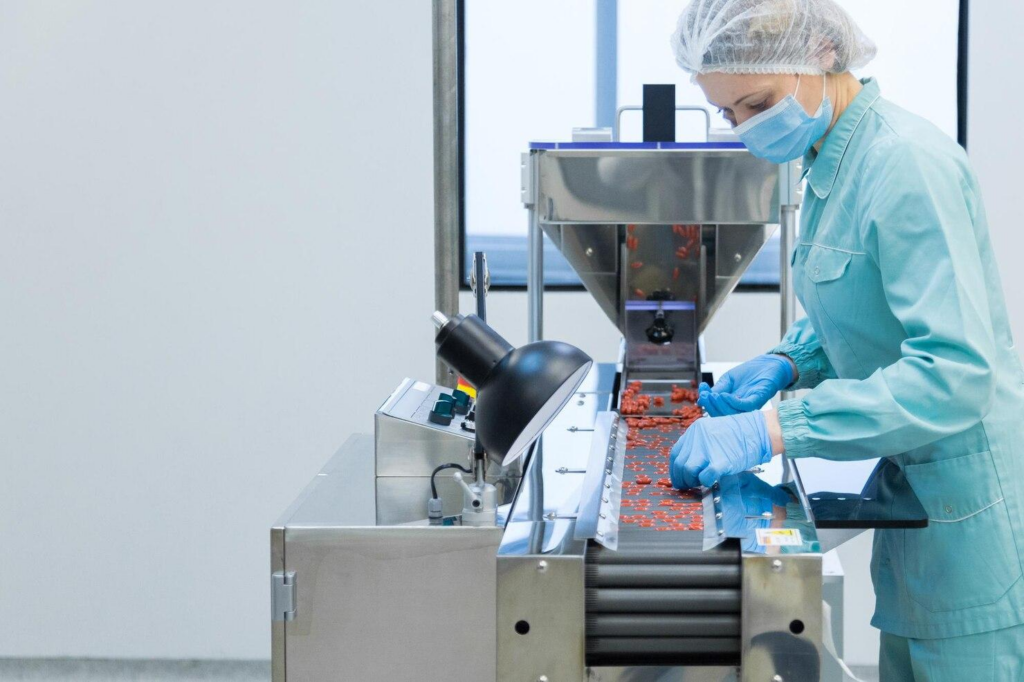

Once you understand the different types of food packaging machines available, the next step is selecting the one that best fits your production needs. Choosing the right machine is not just about capacity—it’s about aligning performance, flexibility, and long-term value with your business goals. Below are the key factors to consider when selecting an automatic food packaging machine.
1. Match the Machine to Your Product Type
Start by evaluating what you are packaging. Liquids, powders, frozen foods, and solid snacks all require different filling and sealing technologies. Consider your product’s size, weight, texture, and sensitivity to ensure the machine can handle it accurately without causing spills, breakage, or waste.
2. Define Your Production Volume and Speed Requirements
Packaging speed directly affects productivity and delivery timelines. High-volume operations may need machines capable of continuous, high-speed output, while smaller or growing businesses may benefit from flexible machines that allow easy scaling. Choose a speed range that supports both current demand and future growth.
3. Balance Budget with Long-Term ROI
While advanced food packaging machines offer automation and efficiency, it’s important to look beyond the upfront price. Consider total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, downtime, and waste reduction. A slightly higher initial investment can often deliver better returns over time.
4. Evaluate Customization and Flexibility
Modern food businesses often manage multiple SKUs and packaging formats. Machines that support adjustable bag sizes, different materials, or quick changeovers can significantly reduce downtime and improve operational flexibility as your product range expands.
5. Choose a Reliable Supplier
Finally, partner with a packaging machine supplier that has proven industry experience. Look for clear technical documentation, strong after-sales support, and real-world case studies. A reliable supplier helps ensure smooth installation, operator training, and long-term performance.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right food packaging machine today requires looking beyond price alone. In 2026, successful packaging lines must also support sustainability goals and smart factory integration.
Food packaging equipment is a long-term investment that directly affects efficiency, cost control, and competitiveness. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront price, helps avoid hidden expenses from downtime, waste, and energy loss. At CHLB Group, we help food manufacturers select scalable, future-ready packaging solutions built for high OEE and regulatory compliance.
Visit https://chlbgroup.com/
to consult with our experts and build a packaging line that supports your growth with confidence.
FAQs
1. What is the most suitable packaging machine for small food businesses?
For small businesses, a pouch-filling machine or vacuum packaging machine is often the best choice due to their affordability and ability to handle small to medium batches efficiently.
2. How do I know if an industrial food packaging machine is right for my business?
Match the machine’s capabilities with your product’s packaging needs, volume, and budget. Reading reviews and consulting with suppliers can also help ensure you choose the right one.
3. Can automatic packing machines handle multiple products?
Yes, many automatic food packaging machines come with adjustable settings to handle different product types, sizes, and packaging materials.
4. Are there machines that can handle both wet and dry food?
Yes, some industrial packing machines are versatile enough to handle both wet and dry foods, though you may need specialized models depending on your product’s requirements.
5. What’s the average lifespan of a commercial food packaging machine?
Most high-quality machines last between 5 to 10 years with proper maintenance. Regular servicing and care can extend the machine’s life and efficiency.